F.1 This appendix provides guidance regarding the risk based certification considerations for the installation of non-rechargeable lithium batteries, or equipment that uses non-rechargeable lithium batteries on Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) part 23 airplanes.
F.2 The regulations applicable to the subject include 23.2510 and 23.2525 amendment 23-64, or 23.1309 and 23.1353 with an earlier amendment level.
F.3 Section 23.1309 requires installed equipment perform its intended function and that it is designed to mitigate the hazard severity accordingly.
F.4 Section 23.1353 requires that storage batteries be designed and installed to maintain safe cell temperatures and pressures that no explosive or toxic gases can accumulate in hazardous quantities, and that corrosive fluids or gases cannot damage surrounding structures or essential systems.
F.5 Section 23.2510 requires the probability and failure conditions of installed system or equipment remain an acceptable inverse relationship.
F.6 Section 23.2525 requires the power supply is adequate for intended operations that a single failure cannot stop power supply to essential loads for safe flight and landing, and has enough power storage capacity of duration to continue safe flight and landing.
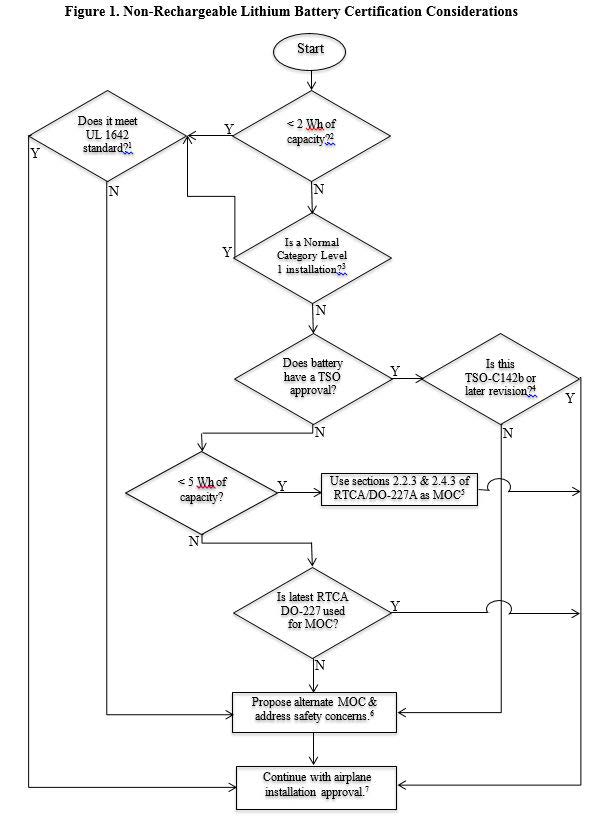
F.7 The following depiction, figure 1, identifies applicable evaluations for installing equipment using non-rechargeable lithium batteries in part 23 airplanes.

Other than meeting the UL 1642 Standard, the appropriate regulatory authority that governs Hazardous Materials Transportation will regulate the carriage of uninstalled lithium batteries. For example, the UN regulations (e.g., UN 38.3, etc.) established guidance for safe transportation of lithium batteries.
A Watt-hour (Wh) is defined as the rated capacity (in ampere-hours, Ah) times the nominal battery voltage. Evaluate the energy of the entire battery capacity for 2 Wh threshold.
Section 23.2005(b) (1), amendment 23-64, defines a Normal Category Level 1 airplane. Certification basis with earlier amendments should use a Class I airplane, as defined in AC 23.1309-1E for this evaluation.
The following is applicable to this footnote:
New installations with TSO-C142a approved articles should present data (e.g., test reports, quantitative and qualitative analysis, etc.) to show that there are no performance gaps in meeting TSO-C142b requirements. One example is substantiation of thermal runaway containment.
TSO-C142b-7 marking (i.e., marking requirements of “-7” described in paragraph 4.b of TSO-C142b) is an acceptable means of compliance for installation.
The following items are applicable to this footnote:
Battery (or cell) must meet at a minimum UL1642 and UN 38.3 requirements. RTCA document, DO-227A, section 2.2.3 and 2.4.3 can be used as a MOC for the end item that the battery (or cell) provides power to.
If RTCA document, DO-227A, sections 2.2.3 and 2.4.3 are not used as a MOC, then the applicant must propose alternate methods to show compliance.
The following items are applicable to this footnote:
New installations that use earlier version of RTCA/DO-227 as a MOC must perform adequate analysis and present additional data to meet the latest standards.
Coordinate with the small airplane standards branch for proposed alternate MOC, or any analysis used to justify deviations from latest DO-227 required tests.
Identified safety concerns must be addressed. Examples are risk assessment and mitigation of internal failures, overheat conditions, flammability, and gas emission.
Continue the certification process. For example, 23.2510 (or 23.1309) compliance includes System Safety Assessment (SSA) process. Location related hazards (e.g. designated fire zones etc.), with respect to where an equipment is to be installed, should be addressed by SSA zonal safety analysis (ZSA), particular risk analysis (PRA), and failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA).